We continue with our second important post workout recovery aid which are supplements. A reminder that all 4 elements (nutrition, supplements, rest and mindset) need to come in play together for our recovery to be maximized.
POST WORKOUT SUPPLEMENTS
After an intense session, you feel sore and tired. Both body and mind feel tired. To help counteract the injuries and burn out that may occur from over training especially if you are new to that type of exercise, you need to implement some solid nutritional strategies to help you recover faster, reduce inflammation, prevent damage to your tissues, improve strength and energy.
High intensity, excessive or explosive exercise like CrossFit can result in oxidative stress, muscle fatigue and muscle injury. It is also common to experience impaired immune system function, immune suppression, infection and excessive inflammation during the recovery period. Often we need additional support with nutritional supplements and proper preventative measures. http://www.jissn.com/content/11/1/61
If you want to start a supplement regime it is advised to introduce each new supplement separately and giving your body the time to adjust. It is not unusual to have adverse reactions to pills so taking them separately will allow you to pinpoint
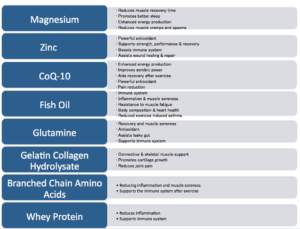
Recommended supplements are:
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Co Enzyme Q10 (CoQ-10)
- Fish Oil
- Glutamine
- Branched Chain Amino Acids
- Gelatin Collagen Hydrolysate
- Whey Protein
Magnesium
Supplementation with magnesium can help improve muscular strength and muscle metabolism. Its benefits include everything from energising our bodies, helping muscles recover to promoting better sleep.
WHAT IS MAGNESIUM? WHICH TYPE IS BETTER?
Magnesium is either a structural cofactor or is responsible for activating over 300 metabolic reactions in the body. It is essential in many processes including protein synthesis, fatty acid oxidation and energy production and storage. Around 95% of magnesium within cells are associated with and essential for cellular energy production and storage. This is mostly due to their association with ATP or ADP (cellular forms of energy), their associated enzymes; their role in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Magnesium deficiency (hypomagnesaemia) in muscles are common in those who regularly exercise, due to increased use and demand, increased loss of magnesium through urine and sweat and poor dietary intake of magnesium. In terms of absorption and use, Magnesium Bisglycinate is the better choice of supplemental magnesium. Magnesium Bisglycinate is simply magnesium that has been bound to glycine molecules. Glycine is the smallest amino acid and as a general rule, amino acid chelates offer the best delivery of minerals within the body.
Benefits of Magnesium
- Reduces muscle recovery time
- Promotes better sleep
- Enhanced energy production
- Reduces muscle cramps & spasms
References:
- Rude RK, Singer FR, Gruber HE. Skeletal and hormonal effects of magnesium deficiency. J Am Coll Nutr, 2009;28(2):131-141.
- Schindler R, et al. The role of magnesium in the generation and therapy of benign muscle cramps. Arzneimittelforschung 1998 Feb; 48(2): 161-6.
- Lukaski HC. Magnesium, zinc, and chromium nutriture and physical activity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Aug; 72(2 Suppl): 585S-93S.
- Schuette SA, Lashner BA, Janghorbani M. Bioavailability of magnesium diglycinate vs magnesium oxide in patients with ileal resection. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1994 Sep-Oct; 18(5): 430-5.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential trace mineral which contributes to growth, development, wound healing and immune function amongst many other things. It’s one of our favourite supplements for CrossFit recovery and zinc deficiency is common amongst all ages so well worth further investigation.
It is an antioxidant that helps to neutralise and remove free radicals from the body which cause inflammation and damage to cells. Even a mild deficiency in zinc can contribute to delayed healing, low testosterone, low muscle mass and recurrent infections.
WHAT IS ZINC? WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT?
Zinc is a cofactor in more than 300 enzymes influencing various organ functions. Prolonged bouts of exercise and heavy training schedules can result in immune system suppression. A suppressed immune system can increase your risk of microbial infections. It decreases the number of white blood cells (T-helper1 lymphocytes) available to attack bacteria, viruses, fungi and cancer cells. Zinc is critical for healthy immune system function. Many factors contribute to poor absorption and deficiency of zinc such as reduced dietary intake, high alcohol and /or high sugar intake (increases Zn excretion). Others factors include iron supplementation and toxic levels of cadmium, gastrointestinal tract abnormalities, abnormalities in zinc transport, age, a high phytate diet (found in some grains and legumes) and use of the oral contraceptive pill.
Benefits of Zinc
- Powerful antioxidant
- Supports strength, performance & recovery
- Boosts immune system
- Assists wound healing & repair
References
- http://www.nature.com/icb/journal/v94/n2/full/icb2015109a.html
- http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/72/2/585s.full
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24488209
Co Enzyme Q10 (CoQ-10)
CoQ-10 is a fat-soluble compound primarily made by the body. It exists in all cells and supports sports performance, improving stamina, endurance and exercise recovery. In aerobic energy production, CoQ10 is vital.
A study has shown that 94% of athletes who supplemented with CoQ-10 felt they had improvement in performance and recovery time. Rich sources of CoQ10 are found in meat, poultry, fish and nuts. Modest amounts are found in fruits, vegetables, eggs, and dairy products. However… Most people consume less than 10 mg/d daily. Around 14-32% of coenzyme Q10 levels are decreased in food by frying. Huge portions of food is required to provide only 30 milligrams of Coenzyme Q-10.
WHAT IS CoQ-10? WHEN IS BEST TO TAKE IT?
CoQ-10 is involved in the transferring of electrons within the Electron Transport Chain and hence the production of energy (ATP). CoQ-10 influences the health and quality of cell membranes and DNA and stimulates cell growth and inhibits cell death. The form of Co-Q10 is important as its absorption into tissues (plasma, skeletal tissue etc) is often slow and limited. CoQ10 is highly susceptible to oxidation, thermal decomposition and photo-degeneration. Co Q10 is soluble in fat, therefore the absorption of supplemental CoQ10 is improved if taken with a fatty meal or mixed with a lipid carrier such as VESIsorb. In one study it was reported that only about 2–3% of orally-administered CoQ10 was absorbed.
Benefits of CoQ-10
- Enhanced energy production
- Improves aerobic power
- Aids recovery after exercise
- Powerful antioxidant
- Pain reduction
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2315638/
Fish Oil (Omega 3)
Fish oil supplementation has been shown to improve immune system function and and reduce the risk of infection due to immunodeficiency post exercise.
Studies (1) have shown that heart rate recovery is also improved by fish oil intake post exercise which leads to a more efficient heart function. However… Not all fish oil supplements are the same: Lower-grade fish oil supplements can be contaminated with heavy metals, dioxins, polychlorinated biphenols (PCBs), or other toxins which are inflammatory to the body and mind. Choose your fish oil wisely and from reputable brands. A rule of thumb is to avoid bulk buy, cheap fish oil brands.
WHY FISH OIL?
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), the major omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil, reduce the inflammatory response caused by exercise as well as decrease delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and increase the rate of recovery. Fish oil consumption has been shown to increase effectiveness of muscle oxygen uptake and therefore resistance to muscle fatigue. It has also shown to reduce inflammatory markers and improve lung function before and after exercise.
Benefits of fish oil
- Immune system
- Inflammation & muscle soreness
- Resistance to muscle fatigue
- Body composition & heart health
- Reduced exercise induced asthma
References
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25355484
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4154279/
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20691135
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16424411
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17490962
Glutamine
Glutamine is your friend if you experience muscle soreness after a workout. It has been shown to quicken recovery rate and reduce muscle soreness particularly after eccentric exercise where you push your muscles beyond their normal point of failure.
Glutamine protects the body against oxidative stress, muscle fatigue and muscle injury which is often associated with high intensity, excessive or explosive exercise training. Note: Glutamine comes in two forms, L-Glutamine which is derived from vegetables and Glutamine which is synthetic.
WHY GLUTAMINE?
Periods of heavy training and prolonged exercise often results in a decrease in plasma glutamine concentration. This deficiency has been associated with impaired immune system function and increased risk of infection. Glutamine supplementation can help counteract these negative side effects. Glutamine is anti-inflammatory and helps to reduce intestinal permeability (leaky gut) that can be induced by exercise.
Benefits of glutamine
- Recovery and muscles soreness
- Antioxidant
- Assists leaky gut
- Supports immune system
References
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25811544
- http://www.jissn.com/content/11/1/61
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25062931
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18806122
Gelatin Collagen Hydrolysate
Most of us focus on building lean muscle and burning fat and ignore our joint and connective health. Collagen hydrolysate has been shown to have a anabolic (growth promoting) effect on cartilage tissue and can reduce joint pain and as a result improve overall sports performance.
You can get collagen via homemade bone broths and supplementation.
WHY GELATIN COLLAGEN HYDROLYSATE?
Exercise can affect the extracellular matrix (ECM) of muscle, tendon and ligaments. ECM provides structural and biochemical support. Daily intake of collagen for up to 6 weeks has been shown to enhance resilience to stress following resistance exercise and improve biochemical markers of connective and skeletal muscle tissue.
Benefits of Collagen
- Connective & skeletal muscle support
- Promotes cartilage growth
- Reduces joint pain
References
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4271657/
- http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1185/030079908X291967
BCAAs (Branched Chain Amino Acids)
BCAAs have been shown to benefit recovery post-training, either from muscle damage or fatigue.
From the nine “Essential” amino acids three of these are the branched chain amino acids; L-valine, L-leucine and L-isoleucine. BCAA’s are mostly found in protein rich foods, such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk and cheese.
WHY BCAAs?
Oxidative stress is associated with chronic inflammation and skeletal muscle wasting. BCAA along with other sulphur-containing amino acids, such L-taurine has been shown to reduce inflammatory responses and the delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and muscle damage created by strenuous exhaustive exercise. 100mg/kg body weight of BCAA supplementation has been shown to delay onset muscle soreness (DOMS) prior to resistance squat exercise. BCAA supplementation has been shown to reduce the drop in plasma L-glutamine concentration and also reduce suppression of the immune system caused by exercise.
Benefits of BCAAs
- Reducing inflammation and muscle soreness
- Supports the immune system after exercise
References
Whey Protein
Most of us would have heard of the benefits of supplementing with protein after exercise with whey protein being the most advertised. Whey proteins are rapidly digested and absorbed and have an amino acid profile that is very similar to that found in skeletal muscles.
Whey contains up to 26% of branch chain amino acids (BCAA), plus L-arginine, L-lysine and L-glutamine – see the benefits of BCAAs above. However… Not all whey protein supplements are created equal: Many of the high street bought protein supplements contain added fillers, thickeners and artificial sweeteners to name but a few suspect ingredients. Always read the label, if you don’t recognise the ingredients then there’s a good chance that your body won’t either. Note: We favour Whey Protein Isolate as most of lactose has been removed which is easier on the stomach for those with dairy intolerance’s/sensitivities.
WHY WHEY PROTEIN?
Whey protein contains the BCAA Leucine, the most anabolic (growth promoting) amino acid, and Cysteine has been shown to help boost levels of the cellular antioxidant Glutathione. Glutathione is an important antioxidant that helps prevent the inflammation and oxidative damage to cells caused by exercise. Whey protein supports the immune system by maintaining the metabolic processes (redox: electron status) in immune cells.
Benefits of Whey Protein
- Reduces inflammation
- Supports immune system
References